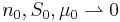Normal-gamma distribution
| Parameters | 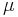 location (real) location (real)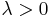 (real) (real)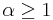 (real) (real)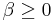 (real) (real) |
|---|---|
| Support | 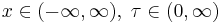 |
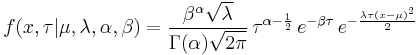 |
|
| Mean | [1] 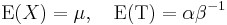 |
| Variance | [1] 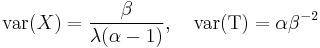 |
In probability theory and statistics, the normal-gamma distribution is a bivariate four-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. It is the conjugate prior of a normal distribution with unknown mean and precision.[2]
Contents |
Definition
Suppose
has a normal distribution with mean 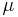 and variance
and variance 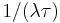 , where
, where
has a gamma distribution. Then 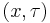 has a normal-gamma distribution, denoted as
has a normal-gamma distribution, denoted as
Characterization
Probability density function
Properties
Scaling
For any t > 0, tX is distributed 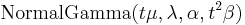
Marginal distributions
By construction, the marginal distribution over  is a gamma distribution, and the conditional distribution over
is a gamma distribution, and the conditional distribution over  given
given  is a Gaussian distribution. The marginal distribution over
is a Gaussian distribution. The marginal distribution over  is a three-parameter Student's t-distribution.
is a three-parameter Student's t-distribution.
Posterior distribution of the parameters
Form of the posterior for a Normal random variable with a Normal-Gamma prior:
Presume the following hierarchy for a normal random variable X with unknown mean 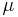 and precision
and precision 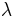 .
.
Where:
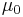 is the prior mean
is the prior mean
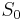 is the prior sum of squared errors
is the prior sum of squared errors
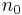 is the prior sample size
is the prior sample size
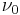 is the prior degrees of freedom
is the prior degrees of freedom
Note the joint distribution of the parameters is Normal-Gamma. The posterior distribution of the parameters can be analytically determined by Bayes' rule working with the likelihood 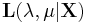 , and the prior
, and the prior 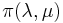 .
.
where 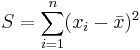 , the sum of squared errors.
, the sum of squared errors.
Now consider the prior,
The posterior distribution of the parameters is proportional to the prior times the likelihood.
Notice the right half begins to look like the kernel of a normal pdf and the left like a gamma. After a bit of juggling and completing the square the result will appear.
This is a normal gamma pdf with parameters 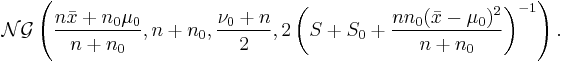
The reference prior is the limiting case as
and 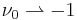
Generating normal-gamma random variates
Generation of random variates is straightforward:
- Sample
 from a gamma distribution with parameters
from a gamma distribution with parameters 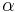 and
and 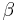
- Sample
 from a normal distribution with mean
from a normal distribution with mean 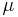 and variance
and variance 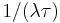
Related distributions
- The normal-scaled inverse gamma distribution is essentially the same distribution parameterized by variance rather than precision
- The Normal-exponential-gamma distribution
Notes
References
- Bernardo, J.M.; Smith, A.F.M. (1993) Bayesian Theory, Wiley. ISBN 0-471-49464-X
- Dearden et al. Bayesian Q-learning, Proceedings of the Fifteenth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-98), July 26–30, 1998, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
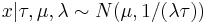
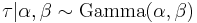
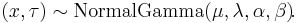
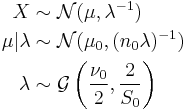
![\begin{align}
\mathbf{L(\lambda, \mu | X)} & \propto \prod_{i=1}^n \lambda^{1/2} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}(x_i-\mu)^2] \\
& \propto \lambda^{n/2} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}\sum_{i=1}^n(x_i-\mu)^2] \\
& \propto \lambda^{n/2} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}\sum_{i=1}^n(x_i-\bar{x} %2B\bar{x} -\mu)^2] \\
& \propto \lambda^{n/2} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}\sum_{i=1}^n\left((x_i-\bar{x})^2 %2B (\bar{x} -\mu)^2\right)] \\
& \propto \lambda^{n/2} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}\left(S %2B n(\bar{x} -\mu)^2\right)]
\end{align}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/de8f1345905ee2a4d7e054d2f3f5e5cf.png)
![\mathbf{\pi}(\mu,\lambda) \propto \lambda^{1/2}\exp[\frac{-\lambda n_0}{2}(\mu-\mu_0)^2] \lambda^{\frac{\nu_0}{2}-1}\exp[\frac{-\lambda S_0}{2}]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/b8fa779783975ce05e46fc9200a45a82.png)
![\begin{align}
\mathbf{P(\lambda, \mu | X}) &\propto \lambda^{n/2} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}\left(S %2B n(\bar{x} -\mu)^2\right)]
\lambda^{1/2}\exp[\frac{-\lambda n_0}{2}(\mu-\mu_0)^2] \lambda^{\frac{\nu_0}{2}-1}\exp[\frac{-\lambda S_0}{2}] \\
&\propto \lambda^{\frac{\nu_0%2Bn}{2}-1} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}(S %2B S_0) ]
\lambda^{1/2}\exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}\left(n_0(\mu-\mu_0)^2 %2B n(\bar{x} -\mu)^2\right)] \\
\end{align}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/ba6abd60da028717efb7658fcd01a5f8.png)
![\begin{align}
\mathbf{P(\lambda, \mu | X} )& \propto \lambda^{\frac{\nu_0%2Bn}{2}-1} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}(S %2B S_0) ]
\lambda^{1/2}\exp[\frac{- \lambda}{2} \left(n_0 (\mu^2 - 2 \mu \mu_0 %2B \mu_0^2 ) %2B n(\bar{x}^2-2 \mu \bar{x} %2B \mu^2)\right)] \\
& \propto \lambda^{\frac{\nu_0%2Bn}{2}-1} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}(S %2B S_0 %2B n_0 \mu_0^2 %2B n \bar{x}^2) ]
\lambda^{1/2}\exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2} (n%2Bn_0) \left(\frac{n_0 \mu^2 %2B n \mu^2 }{n %2B n_0} - 2 \mu \frac{n\bar{x} %2Bn_0\mu_0}{n%2Bn_0} \right)] \\
& \propto \lambda^{\frac{\nu_0%2Bn}{2}-1} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}(S %2B S_0 %2B n_0 \mu_0^2 %2B n \bar{x}^2) ]
\lambda^{1/2}\exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2} (n%2Bn_0) \left(\mu^2 - 2 \mu \frac{n\bar{x} %2Bn_0\mu_0}{n%2Bn_0} %2B \left (\frac{n\bar{x} %2Bn_0\mu_0}{n%2Bn_0}\right )^2 - \left (\frac{n\bar{x} %2Bn_0\mu_0}{n%2Bn_0}\right )^2\right)] \\
& \propto \lambda^{\frac{\nu_0%2Bn}{2}-1} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}\left(S %2B S_0 %2B n_0 \mu_0^2 %2B n \bar{x}^2 - \frac{\left (n\bar{x} %2Bn_0\mu_0 \right )^2}{n%2Bn_0}\right) ]
\lambda^{1/2}\exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2} (n%2Bn_0) \left ( \mu - \frac{n\bar{x} %2Bn_0\mu_0}{n%2Bn_0}\right )^2] \\
& \propto \lambda^{\frac{\nu_0%2Bn}{2}-1} \exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2}\left(S %2B S_0 %2B \frac{nn_0 (\bar{x}-\mu_0)^2}{n%2Bn_0}\right) ]
\lambda^{1/2}\exp[\frac{-\lambda}{2} (n%2Bn_0) \left ( \mu - \frac{n\bar{x} %2Bn_0\mu_0}{n%2Bn_0}\right )^2] .\\
\end{align}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/14044b908f97daaccb44ba8f73b7644b.png)